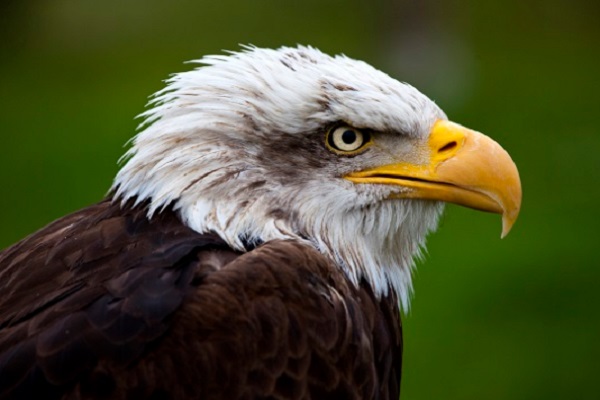
An adult bald eagle, young ones do not have white plumage in the head and tail.
o
o
Cool facts about the bald eagle
- The Bald Eagle has been the national emblem of the United States since 1782.
- Benjamin Franklin did not approve of the bald eagle as the US emblem. He thought it lacked courage, had bad moral character and did not get his living honestly.
- Bald eagles are not really bald. Their head is white, but their name actually comes from the old English word piebald which meant “white headed” rather than hairless.
- They are a sacred bird in some Native American cultures. Their feathers are used in traditional ceremonies.
Population and Conservation Status
- The IUCN Red List of Threatened lists the bald eagle as Least Concern as its population has an increasing trend.
- This species has experienced a 779% increase over the last 40 years.
Taxonomy
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Aves
- Order: Accipitriformes
- Family: Accipitridae
- Species: Haliaeetus leucocephalus
Name
- Common name: Bald eagle
- Scientific name: Haliaeetus leucocephalus
Distribution and Habitat
- Bald eagles are native to Canada, United States, Mexico and Saint Pierre and Miquelon. This species has an extremely large range.
- They live near the water favoring coasts and lakes where there is plenty of fish.
- In the 1950s the number of bald eagles in North America declined to as low as 500 individuals. DDT contamination, predation and hunting were causes of their decline.
- In 1967 the bird was declared an endangered species in the United States. Conservation efforts allowed the species to be removed from the Endangered Species Act in 2007.
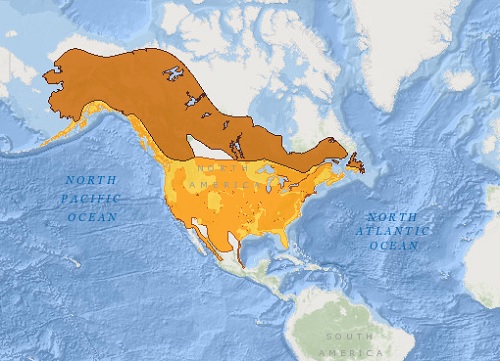
Bald eagle distribution map. Adapted from IUCN .♦resident ♦breeding
Physical Features
- Bald eagles are birds of prey and it is considered the second largest raptor in North America after the California condor.
- Adult birds have white plumage in their head and tail and brown in the rest of their bodies. Young birds are dark and lack the lighter plumage that adults have until they are about 4 to 5 years old.
- They do not have plumage in their legs and have powerful talons.
- Their large yellow and hooked beaks.
Size and Length
- Male bald eagles have a body lengh of 28 to 40 inches (70-102 cm).
- Their wingspan is between 5.9 to 7.5 feet (1.8 – 2.3 m).
- They weight approximately from 6.6 to 13.9 lb (3 to 6.3 kg)
- Females are about 25% larger than males.
Behavior
- These birds spend hours standing on trees overlooking the water alert for feeding opportunities.
- Bald eagles are opportunistic carnivores. Their diet consists mostly of fish, about 60%, small mammals, birds and carrion.
- These birds often steal their food from other birds and occasionally from mammals such as otters. They use their powerful talons to fish.
- They are solitary birds, however they congregate at feeding sites.
- These birds avoid human interaction.
Reproduction
- Sexual maturity is reached at 4 to 5 years.
- Bald eagles are monogamous and are believed to mate for life.
- They build the largest nests of any North American bird, about 5 to 6 feet in diameter and 2 to 4 feet tall. They build their nests in tall trees above the forest canopy.
- Both male and female bring material to build the nest and can take up to three months to complete, some nests are reused.
- Bald eagles lay two to three eggs. Both parents take turns incubating the eggs for about 35 days.
- Young birds stay with they parents for approximately one month.
Life Expectancy
- The longest living bald eagle in captivity was 48 years old.
- In the wild they live over 40 years.
References and further research
IUCN Red List of Threatned Species – Haliaeetus leucocephalus
The Cornell Lab of Ornithology
The Animal Aging and Longevity Database – Haliaeetus leucocephalus
Smithsonian National Geological Park
Greater Vancouver Zoo – Bald Eagle
University of Michigan Museum of Zoology – Haliaeetus leucocephalus

