African Elephant mother and calf. The African elephant is listed as a vulnerable species by the IUCN.
Name
- Common name: African elephant
- Scientific name: Loxodonta africana
Physical Features
- African elephants are the largest and heaviest land mammals on earth.
- They have larger ears than the Asian elephant and they are shaped like the continent of Africa. Each ear can measure 4 ft or 1.2 m across. Their large ears are used to control their body temperature. They contain capillaries helping release heat.
- Males and females have visible tusks with no difference in length. They grow up to 10 ft or 3 m long and weigh 130 lb or 60 kg each. Tusks are overgrown incisor teeth in the upper jaw and they serve as weapons or tools.
- Tusks grow continuously since they are 6 months old. Elephants have a dominant left or right tusk just like humans are right or left handed. The dominant tusk is shorter and its tip is more rounded because they wear out.
- African elephants have dark grey skin which is very wrinkly. Their skin is thick and tough and can be 1 in or 2.54 cm thick. Even though it is thick it is also very sensitive. They use mud as sunscreen and as insect repellent.
- The African elephant has a concave back as opposed to the Asian elephant that has a convex back.
- The trunk or proboscis is used for picking up objects, touching, breathing and producing sounds. It can measure about 5 f or 1.5 m long and weigh 300 lb or 135 kg. The trunk is so strong that it is able to lift up to 770 lb or 350 kg.
- African elephants have at the end of their trunk two finger-like extensions allowing them to pick food up
- Elephants have 26 teeth and 6 sets of molars during a lifetime. Molars do not grow vertically as in most mammals but they develop horizontally from behind pushing the old worn out molar forward.
Weight and Height
- African elephants measure from 10 to 13 ft or 3 to 4 meters tall.
- They weigh from 8,800 to 15,400 lbs or 4,000 to 7,000 kg.
Species
- Genetic evidence suggests that there may be at least 2 species of African elephants, the Savanna elephant (Loxodonta africana africana) and the Forest elephant (Loxodonta africana cyclotis). According to The African Elephant Specialist Group more research is necessary for its reclassification which might leave species unprotected.
- Savanna elephants (Loxodonta africana africana) are found in grasslands and are the largest of all elephant species. Their tusks are curve out and forward.
- Forest elephants (Loxodonta africana cyclotis) live in forests. They are slightly smaller than the African savanna elephants but larger than its Asian relatives. Their tusks are pointed straight down.
Distribution and Habitat
- African elephants are found south of the Sahara Desert in 37 countries. Its distribution is becoming increasingly fragmented across the continent.
- They are regionally extinct in Burundi, Gambia and Mauritania.
- They have a wide range of habitats from dense forests to savannas, arid deserts, river valleys, marshes, swamps and grasslands.
- African savanna elephants live in grasslands and bushlands.
- African forest elephants live in the equatorial forests of central and western Africa.
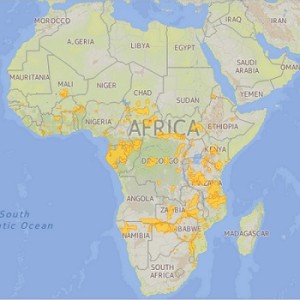
Distribution of the African Elephant. Source: IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
Behavior
- Elephants roam in herds and are organized into a social matriarchal community of about 10 to 20 individuals. The matriarch is the oldest female. Asianelephant herds are smaller ranging from 8 to 12 individuals.
- These family units join other families forming bond groups which may number over 100 individuals.
- Herds are made up of related females and their offspring. Males leave when they reach maturity at around age 12.
- Males live alone or in bachelor herds.
- Elephants are active during the day but in areas where there is human activity they become nocturnal.
- Elephants communicate by touching with their trunks and by producing sounds. They make sounds in low frequency so humans cannot hear some of them. They also growl and rumble.
- They sleep from 3 to 4 hours a day and spend 16 hours a day eating.
- Their home range is similar to the Asian elephant approximately 14 to 52 sq.km.
Diet
- Elephants are herbivores. Their diet includes leaves, roots, bark, fruit and grass.
- They consume from 220 to 660 lb or 100 to 300 kg of food a day.
- They drink up to 190 liters or 50 gallons of water every day.
Reproduction
- Elephants reach reproductive maturity between 10 and 12 years old.
- They breed throughout the year but it is more prevalent during the rainy season.
- Females give birth every 3 to 4 years.
- Gestation lasts 22 months, the largest of any mammal.
- Litter size is 1, rarely 2.
Calves
- Calves are born into a nurturing community of related females.
- For the first 3 months they exclusively drink maternal milk then gradually get introduced to vegetation. They are weaned when they are 2 to 3 years old.
- There is no paternal care of offspring.
- Calves are born 33 in or 85 cm tall and with a weigh of around 260 lb or 120 kg.
Life Expectancy
- The average life expectancy of elephants is 70 years in the wild and 80 years in captivity.
Predators
- Adult elephants have no natural predators other than humans.
- Young elephants on the other hand are at risk or predation by hyenas, leopards, crocodiles and lions.
Threats
- Poaching for meat and ivory are the major threats African elephants face.
- Loss and fragmentation of habitat due to land conversion and rapid growth of human settlements.
- Sport hunting of African elephants.
- Starvation in old age due to lack of teeth.
Conservation Status
- The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species lists the African elephant as a “vulnerable” species.
- The African elephant is listed on Appendix II on the Bonn Convention.
- It is listed on Appendix I of CITES.
Taxonomy
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Proboscidea
- Family: Elephantidae
- Genus: Loxodonta
- Species : Loxodonta africana
References and further research
Natural History Museum – Savanna Elephant
Wildlife Conservation Society – Savannah Elephant
IUCN Red List of Threatened Species – Loxodonta africana
IUCN Species Survival Commission – African Elephant Specialist Group
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service International Affairs – African Elephant Conservation Fund